Our Institute of Radiology is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, enabling us to offer all commonly used diagnostic imaging procedures. Learn more about each examination method, how it works, and in which cases it is used.
Conventional Radiology and Fluoroscopy
In conventional X-ray examinations, X-rays are used to produce two-dimensional images. Fluoroscopy enables image-guided procedures to be performed on the body, for example as part of pain therapy or as preparation for cross-sectional imaging examinations.
What happens during the examination?
During an X-ray examination, two images of the region of interest are usually taken. In exceptional cases, however, only one or several images may be required.
During fluoroscopy, a specialist in radiology is involved and will discuss the planned procedure with you and carry it out after obtaining your consent.
Minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic interventions
As part of interventional radiology, minimally invasive procedures are performed to treat medical conditions using imaging guidance such as fluoroscopy, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These procedures include, among others, organ punctures (e.g. for cell sampling) as well as drainages to remove fluids or pus..
What happens during the examination?
These procedures comprise a wide range of complex interventions and therefore not all interventions can be listed here. If an interventional procedure is required in your case, the specific procedure will be discussed with you in detail by the radiologist performing the intervention.
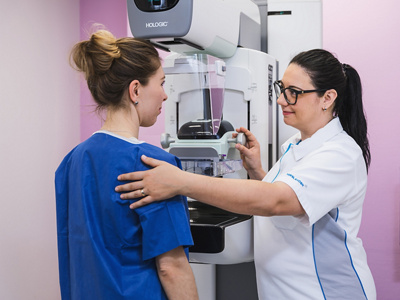
Mammography
Our experienced team of radiologists, specialized in breast diagnostics and interventions, offers a personalized and comprehensive service for the early detection of breast cancer and the evaluation of benign and malignant breast conditions. Patients are examined using state-of-the-art equipment, and in many cases the results can be discussed immediately. We understand our patients’ concerns and provide a compassionate and timely diagnostic assessment.
What happens during the examination?
During a mammography examination, the breast is positioned between the X-ray unit and the image receptor and is then gently compressed with a compression plate for a few seconds to obtain the image. The greater the compression of the breast, the better the image quality and the lower the radiation dose. Two images of each breast are taken in different positions.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound devices create images of the human body using sound waves. These sound waves are far beyond the range of human hearing and are completely harmless to the human organism. Therefore, ultrasound can also be safely used during pregnancy.
The main areas of focus in sonographic diagnostics include the evaluation of the upper and lower abdominal organs, the neck (including the thyroid gland), blood vessels, and the female breast.
Our modern ultrasound systems offer all the advantages of advanced ultrasound diagnostics of the abdomen, joints, and breast, including 3D and panoramic imaging.
Computed Tomography (CT)
An X-ray tube and a detector rotate around the patient, generating a large number of projections. Using mathematical reconstruction processes, these projections are converted into so-called cross-sectional images. From this data set, images can be reconstructed in any body plane or calculated three-dimensionally.
What happens during the examination?
While lying on an examination table, you will be moved through a ring-shaped opening. From there, multiple cross-sectional images of your body are taken using X-rays at millimetre intervals. For certain examinations, you may be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds. You will be informed via an intercom system.
For most examinations, a contrast agent is injected into a vein in your arm. This enhances image contrast and allows better assessment of organs and blood vessels. The warm sensation that may occur is normal. The contrast agents used today are generally well tolerated and are quickly eliminated by the kidneys.
CT is used, among other things, for the following examination
- Imaging of the chest (thorax)
- Visualization of pathological bone structures and detection of even the smallest fractures
- Evaluation of diseases of the abdominal cavity (abdomen)
- Imaging of the skull base, paranasal sinuses, and middle ear
- Detection of calcifications of the coronary arteries
- Examinations for patients with cardiac pacemakers and implanted defibrillators
- Examinations for patients with older cochlear implants (inner ear prostheses)
- Examinations for patients with metal fragments in the body
- Pain therapy of the spine and joints (CT-guided injections)
Various types of interventional procedures

Magnetic Resonance Tomography (MRT/MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging, abbreviated as MR(T) or MRI (from Magnetic Resonance Imaging), is a cross-sectional imaging technique, similar to computed tomography, that allows a clear, superimposition-free view of the inside of the body. However, unlike CT, MRI does not use X-rays but operates with strong magnetic fields.
Magnetic resonance imaging enables imaging of the human body without the use of ionizing radiation (i.e. without X-rays or radioactive substances). Hydrogen atoms in the human body are excited within a magnetic field and, under the influence of electromagnetic radiofrequency fields, generate a specific resonance. This resonance can be converted into images using complex mathematical reconstruction processes.
How do I prepare for an imaging examination?
Before the examination, you will be asked to remove all metallic and magnet-sensitive objects (e.g. jewelry, credit cards, mobile phones, keys, etc.). For certain clinical indications, a contrast agent is injected into a vein during the examination. For this purpose, a venous access will be placed beforehand.
What happens during the examination?
Depending on the body region being examined, the procedure takes between 20 and 90 minutes. For optimal image quality, it is important that you remain still throughout the entire examination. The scanner produces loud knocking noises; therefore, you will be provided with hearing protection and headphones through which you can listen to music.
You can reach the medical staff at any time during the examination by using the emergency call button. The staff can communicate with you at all times via the intercom system.
Why is a contrast agent needed??
MRI contrast agents help differentiate pathological processes from normal tissue, improve image quality, and provide information about blood flow. These contrast agents are generally very well tolerated. If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to contact our medical staff at any time.
What are the advantages of an MRI?
- No exposure to ionizing radiation
- Can also be used in adolescents and children
- In individual cases, possible in pregnant women from the 4th month of pregnancy onward
- Very precise, low-risk, and painless examination that provides detailed diagnostic information with minimal effort
- Visualization of organs and tissues in any desired plane and slice orientation
High contrast between healthy tissue and pathological changes
- Sehr gute Darstellung der meisten Gefässe ohne invasive Methoden
- Excellent visualization of most blood vessels without invasive methods
- Relatively short examination time thanks to modern scanner technology
Excellent tolerability when contrast agents are used
Please note:
MRI emergency examinations are available at short notice as well as outside our regular opening hours.

Cardiac Imaging
The specialized field of cardiac imaging focuses on the assessment of cardiac anatomy, cardiac function, the heart muscle, and the blood supply to the heart.
Examinations are performed and interpreted interdisciplinarily in close collaboration between specialized radiologists and cardiologists. For high-quality diagnostics, state-of-the-art equipment of the latest generations is available. We work with advanced software for post-processing and evaluation of the examinations, enabling functional measurements and detailed anatomical visualization.
At our institute, examinations are carried out using modern, non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging and/or computed tomography, depending on the clinical question. In many cases, this allows invasive diagnostic procedures or tissue sampling to be avoided. Our services include, among others:
Computertomography:
- Quantification of calcifications of the coronary arteries (calcium scoring)
- Contrast-enhanced imaging of the coronary arteries
- Assessment of heart valves and cardiac anatomy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- Assessment of cardiac function
- Evaluation of the heart muscle, e.g. detection of inflammation/myocarditis and scars after myocardial infarction
- Assessment of myocardial blood supply under pharmacological stress
- xamination of heart valves and cardiac anatomy
MRI-guided breast biopsy (vacuum-assisted biopsy)
If a suspicious lesion suggestive of a tumor is detectable only on breast MRI, an MRI-guided breast biopsy is recommended.
How is the biopsy performed??
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia. For the examination, the patient lies in a prone position in the MRI scanner. To precisely localize the area of concern in the breast, a contrast agent is administered. The exact position of the lesion can then be calculated.
After the skin of the breast has been locally anesthetized, a small incision (approximately 3–4 mm) is made. The affected tissue is then removed using a special needle under vacuum assistance. At the end of the procedure, the biopsy site is marked with a small clip. This allows the site to be identified if a repeat biopsy is required or during future mammography or ultrasound follow-up examinations.
In order for the examination to be performed, the patient should be able to lie on her stomach for approximately 30–45 minutes without changing position..
Why is a contrast agent needed?
MRI contrast agents help distinguish pathological processes from normal tissue, improve image quality, and provide information about blood flow. These contrast agents are generally very well tolerated. If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to contact our medical staff at any time.nal.
Special Examinations
In addition to standard examinations, we also offer specialized diagnostic techniques. These allow diseases to be detected at an early stage and, in some cases, treated on an individualized basis. Please contact us for special examination inquiries by phone at +41 41 784 05 90.