The medical specialists at Ortho Clinic Zurich provide a comprehensive range of orthopaedic treatments for the musculoskeletal system. They specialise in the following areas:
Orthopaedics for adults and children
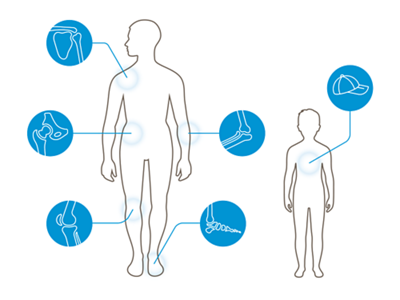

Shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is one of the most flexible joints in the body. Together with the elbow, the shoulder positions the hand for activities above head height. This flexibility comes from the interaction between 3 bones, which together form 5 different joints. The muscles and ligaments contribute to stability and exertion of force.
Regardless of the patient’s age, injuries and changes caused by wear in the joint have a corresponding limiting effect in daily life and in sport. For example, simple tasks at head height are no longer possible.
Many problems can be treated without surgery, i.e. through conservative treatment. If surgical treatment is necessary, nowadays this can normally be arthroscopic or minimally invasive.
Core competencies
Reconstruction
- Arthroscopic and open surgery on tendons including tendon transfers
- Arthroscopic and open surgery in case of shoulder instability
- Osteotomy (changes in the bone position/axis)
- Sports surgery (sports injuries)
Shoulder prosthetics (artificial joints)
- Primary implantation and revision
- Clarification of painful prosthetics
Fracture care (primary and revisions)

Elbow joint
The elbow joint is a combination of 3 bones. In comparison with the shoulder, the elbow is held in position much more tightly by ligaments. However, the muscles play a similarly key guiding role as in the case of the shoulder, namely spatially positioning the hand.
Limitations due to injuries and wear cause similar limitations in everyday life and in sport.
In this context also, an improvement can be expected through conservative therapy in many cases. In addition to classic open surgery, arthroscopic surgery can also be used to treat some illnesses in this context.
Core competencies
Reconstruction
- Arthroscopic surgery for tennis elbow, osteoarthritis, loose joint fragments
- Sports surgery for reconstruction of ligaments (instabilities)
- Reinsertion of ruptured tendons (bicep tendon)
Elbow prosthetics (artificial joint)
- Primary implantation and revision
- Clarification of painful prosthetics

Hip joint
Like the shoulder, the hip is a ball joint with a very large range of motion. It enables a wide variety of movements and it is the link between the torso and the legs. This mobility is enabled by a highly stable holding device consisting of a capsule and ligaments, and overlapping layers of muscles. If the joint has an unfavourable shape, problems can arise even at a young age. Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is an illness that occurs at an older age. The main symptoms of illnesses of the hip joint are typically pain in the groin, which increases with movement and load. There is sometimes also pain in the morning after a period of inactivity. As the condition develops, there are often limitations to daily life, and bending down or putting on socks becomes more difficult.
Core competencies
- Hip joint replacement (prosthetic hip) using a minimally invasive technique (if appropriate a “Bikini” incision)
- Diagnosis and conservative therapy for femoroacetabular impingement

Knee joint
The knee is the largest joint in the human body. It is made up of three bones (femur, the bones of the lower leg, and the kneecap). To withstand varied loads, it is stabilised with several ligament structures and tendons, which still allow a high level of mobility. The two meniscuses also act as damping “shock absorbers”. All joint structures work together to enable a highly complex load with high stability.
With the complex structure, it is understandable that knee problems can present in very varied ways in addition to the main symptom of pain. Changes caused by accidents may cause a feeling of instability. Changes caused by wear can develop slowly over years, and can cause limited mobility, locking, or a tendency to swell.
Core competencies
- Knee joint replacement (knee prosthesis) and partial knee joint replacement (sled prosthesis)
- Artificial knee joint replacement and revision interventions
- Arthroscopic knee surgery (meniscus, cruciate ligament surgery)
- Complex cartilage surgery on the knee using open and arthroscopic techniques including transplantation procedures (AutoCart/"minced cartilage"/ACT)
- Correction interventions for deviations in the leg axis (knock knees, bow legs)
- Surgical care for instabilities of the kneecap (patella luxation)
Core competencies
- Conservative and surgical treatment of knee problems and injuries
- Arthroscopic operations
- Reconstructive surgery and endoprosthetics
- Sports traumatology, sports surgery

Core competencies
- Conservative and surgical treatment of problems and injuries affecting the ankle and foot
- Reconstructive surgery and endoprosthetics
- Sports traumatology, sports surgery

Paediatric orthopaedics
The range of treatments on offer includes all conservative (non-surgical) and surgical paediatric orthopaedics:
- Controlling growth for all types of bow legs, knock knees, or differences in leg length
- Treatment of hip pathologies (Perthes disease, dysplasia, and epiphysiolysis)
- Non-surgical treatment of spine problems (child back pain, scoliosis, kyphosis)
- Foot deformities (clubfoot, pigeon toes, flat feet, etc.)
- Assessment of child’s gait (in-toeing and out-toeing)
- Paediatric fracture treatment and treatment of deformity following fractures (traumatology of children’s musculoskeletal system)
Core competencies
The entire range of conservative and surgical paediatric orthopaedics, particularly all kinds of techniques for controlling bone growth, treatment of hip pathologies, (Perthes disease, dysplasia and epiphysiolysis), conservative treatment of scoliosis and kyphosis. Further specialisations include foot deformities (club foot, pigeon toes, flat feet, etc.), gait evaluation (in-toeing and out-toeing), as well as the entire conservative and operative traumatology of the paediatric musculoskeletal system.
Montag - Freitag
8.00 - 12.00 Uhr
13.00 - 17.00 Uhr